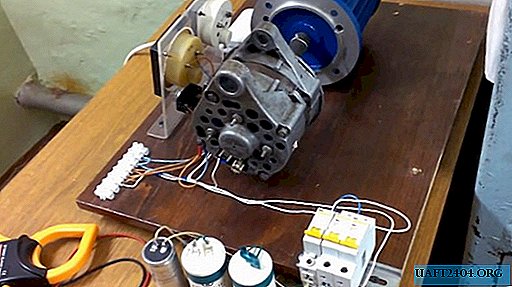
To answer the question of how to choose a capacitor for induction motors and how the capacitors differ from each other, we will assemble a stand from a conventional three-phase motor with a power of 250 watts. As a load, we use a standard generator from a VAZ car.

We connect three different capacitors through the machines. Turning on / off the machines will allow you to check the capabilities of capacitors.

We select a capacitor
For the experiment, we choose three capacitors with a capacity of 10, 20, and 50 microfarads. Our task is to try to start the electric motor from each capacitor in turn.
10 uF capacitor
When connected to a 220 V network and turning on the first 10 microfarad capacitor, the electric motor turns on only after a handshake. Auto start does not occur.

Conclusion: for a 250 W electric motor, a capacitor of 10 microfarads is not enough.
20 uF capacitor
When you try to start the electric motor from a capacitor with a capacity of 20 microfarads, the engine is switched on automatically.

Conclusion: with a capacitance of 20 microfarads, the electric motor started without problems.

50 uF capacitor

When continuing the experiment with a 50 microfarad capacitor, the electric motor starts automatically, however, it works with a high noise level and just shakes.
Conclusion: the capacitance of the last capacitor tested is large for the installed electric motor.
When choosing a capacitor for a low-power three-phase electric motor, give preference to a device with a rated capacity (as in our experiment) corresponding to the motor power. The capacitor of small capacity does not start the electric motor; if the capacitor is too large, it causes the motor to heat up and makes a lot of noise during operation. An experimentally recommended capacitor with a capacity of 20 MkF, which immediately started the engine and did not cause its overheating.
Conclusion
To start a three-phase electric motor in a 220 V network, the working capacitor is selected based on the motor power. With increasing power for every 100 watts, the capacity should increase by 7-10 microfarads. For example, for a 0.5 kW engine, you can choose a capacitor with a capacity in the range of 35-50 MKF.
You also need to consider such a parameter as the rated voltage of the device (that is, the voltage that the capacitor can withstand). In the work, it is recommended to use capacitors with parameters 100% higher than the real voltage applied to the device. For this example, it is 450 V.











